When we talk about the technological revolution, some will think of artificial intelligence, virtual reality or cyborgs like in the movie I, Robot and some more perhaps inspired by teleportation or time travel.
The point is that all that tangible technology or that we can see, has a real technological advance inside that makes it highly revolutionary and for the case of this blog we take Blockchain as an example, which as many of us already know, is the system that supports and allows cryptocurrencies to exist.
The system arises from the need to not have intermediaries or a central server when transmitting data and it can be sent or received directly from person to person or peer to peer, in this way, each user could have control of their information.
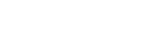
We can see in the image, on the one hand we have the social networks that have control of the information and before it reaches the sender, it goes through their servers, and on the other hand, there is the blockchain that seeks not to have a central:
Now, giving details of the system as such is not very precise without taking into account the following technologies that make blockchain possible:
Cryptography: Basically it refers to hiding a message in plain sight by modifying or altering it so that the information is unintelligible and available only to certain types of users.
P2P or peer to peer: It is a type of connection that allows two people to have communication without the need for intermediaries.
Hash or Hash Function: It is a modified text of numbers and letters that is unique and unrepeatable, and is extracted through software that converts one or more elements into a hybrid as we see in the image box to a 64-character code. The Hash is precisely the pillar of the system because it is the one that allows the blocks to be linked.
Mining: It is the computer process to process transactions, ensure network security and ensure that all participants are synchronized at the same time.
Proof of work: It is a kind of challenge that miners have to achieve the resolution of the computer process to create the block chain as quickly as possible. The miner who wins will have a reward and his block will be the one that is replicated between the other nodes.
Now, to give us an idea, in the previous blog, where we talked about Web 3.0, I briefly mentioned the Blockchain system or chain of blocks as “a data transfer system that travels through multiple nodes or independent servers ( any computer with the appropriate software) that record and validate the information when it leaves one node and enters another without intermediaries (like an income and expense accounting book)”.
This brief description and the example of the programs to download mp3 files and torrents can give us an idea to enter the world of blockchains that in recent years are taking a greater role with the Bitcoin era and other cryptocurrencies.
Although these exchanges do not necessarily have to be in economic matters, it is how their use is currently best known, but the most revolutionary thing comes from within, because the system is so well structured that it has laid the foundations for it to be impassable, immutable , indelible and even invulnerable, or rather, quickly detectable when someone wants to hack it.
Let’s consider a simple flow of cryptocurrencies to understand it better:
- 3 transactions are presented.
- Transactions trigger miners to begin the proof-of-work computing process to create blocks.
- Blocks are formed from transactions, for example: Transaction 1: A ⇢ B, Transaction 2: C ⇢ D, Transaction 3: D ⇢ E are grouped together and form a block.
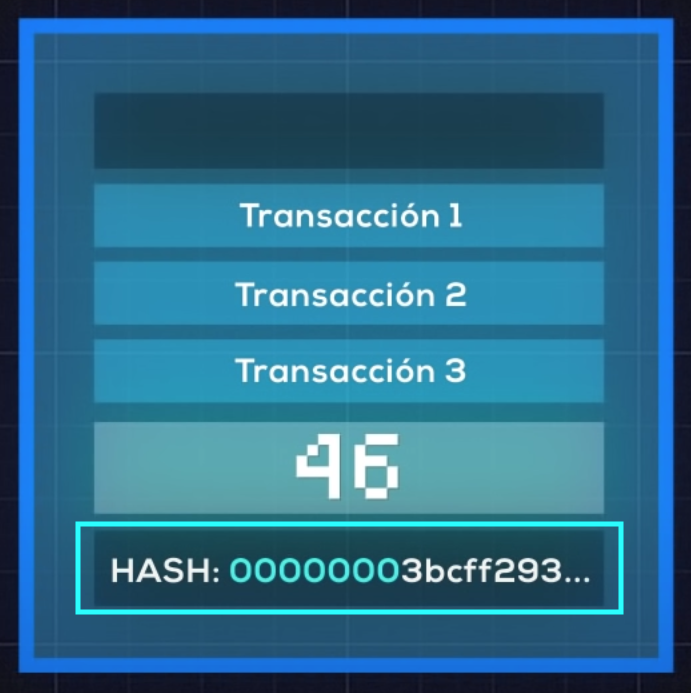
- Once this happens, the system seeks to assign a Hash based on the data entered (of the transactions) or alphanumeric code to finish consolidating the block.
- Once the hash is found, the block is closed and it is linked to the next block and so on, successively forming the chain of blocks as we can see in the image.

Now, how do we know that it is not possible to violate the chain of blocks? Well, very simple, because as the Hash is resolved based on the information of the transactions, when someone wants to change some data of block 42, for example, then the Hash will change and this will change all the following blocks, but since all the nodes has a copy, then they will have to be changed in all of them, something that is impossible because the rest of the nodes would notice the alteration and discard the operation.
Also, because it would need a computational process on a universal scale to do it and to always be able to beat the other nodes that are working to continue creating blocks, so it would have to complete the entire chain and then beat the rest, and it is impossible to achieve right now.
As we see in the image, once you start to exploit a block, then the rest changes, because the hash that chains them also changes. And we are talking about a single node, not the entire network that has an equal copy.

#aplicaciones #blockchain #development #nft
Last modified: February 9, 2022